question id: Poly01
Chap 26 Review
\[ \newcommand{\dnorm}{\text{dnorm}} \newcommand{\pnorm}{\text{pnorm}} \newcommand{\recip}{\text{recip}} \]
Exercise 1 In the polynomial \(a_0 + a_x x + a_y y + a_{xy} xy\), what is the term \(a_{xy}xy\) called?
Exercise 2 In the polynomial \(a_0 + a_x x + a_y y + a_{xx} xx\), what is the coefficient on the interaction term?
question id: Poly02
Exercise 3 Imagine a second-order polynomial in three inputs: \(x\), \(y\), and \(z\), like this: \[b_0 + b_x x + b_y y + b_z z + b_{xy} xy + b_{xz} xz + b_{xx} x^2 + b_{yy} y^2 + b_zz z^2\ .\] All of the possible second-order (or less) terms are shown, except for one. Which term is missing?
the interaction between \(y\) and \(z\)
the quadratic term in \(z\)
the linear term in \(y\)
the constant term
question id: Poly03
Exercise 4 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 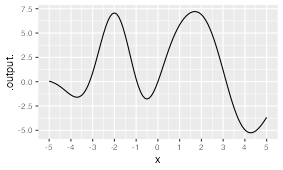
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=-2,\) what will be the sign of the coefficient on the first-order term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly04
Exercise 5 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=1\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the first-order term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly05
Exercise 6 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=1\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the second-order term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly06
Exercise 7 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=-4\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the first-order term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly07
Exercise 8 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=4\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the second-order term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly08
Exercise 9 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=4\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the constant (zeroth-order) term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly09
Exercise 10 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=3\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the second-order term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly10
Exercise 11 Here is a function \(f(x)\): 
In the Taylor polynomial approximation to \(f(x)\) centered at \(x=0\), what will be the sign of the coefficient on the reciprocal term. Choose the best answer.
question id: Poly11
Exercise 12 Here is a function \(g(x)\): 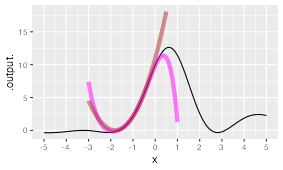
Two Taylor polynomials, centered on the same \(x\) are shown. One is fifth-order, the other is third-order. Which is which?
question id: Poly12
Exercise 13 Here is a function \(g(x)\): 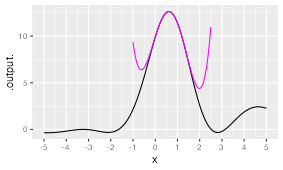
with a Taylor polynomial shown in magenta. What is the order of the polynomial?
question id: Poly13