Math in Stats
Unnatural mathematics
There’s an unhealthy relationship between math education and stats education. Some examples:
- Calculus pre-requisite for stats. Why?
- Are we doing integrals and derivatives in stats?
- Calculus not needed for “area under a curve.” And there’s already too much emphasis on probability distribution puzzle solving.
- Complex algebraic formulas used to express ideas.
- Do students assimilate the formulas?
- Are students empowered by the formulas?
- Are the formulas needed to do stats?
- Statistics is seen as a way to circumvent ineffective and harmful remedial math courses. > Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different results.
- Graphing calculators
In comparison … Math topics that are naturally prompted by stats
- functions
- derivatives
- linear algebra – See MathFest 2019 talk
- trees and graphs
- operator composition
Math Topic I: Functions
Instead of arithmetic, introduce models that are functions:
Statistical model:
- A function that turns inputs into an output.
- Inputs: values of explanatory variables
- Output: a (model) value for the response variable.
Settings:
- Quantitative output with one quantitative and one categorical input.
- Quantitative output with two categorical inputs.
- Quantitative output with two quantitative inputs.
Little App: Regression.
- Example: height ~ age + sex.
- Add in interactions
- Add in nonlinearity
Math Topic II: Effect sizes
a.k.a. finite differences and partial derivatives
Effect size:
- Describes a statistical model
- Choose one input
- Evaluate the model at two values of that input, holding the others constant
- Look at change of output (or, change of output divided by change in input).
It’s not about slopes, it’s about how an output changes when an input changes.
Math Topic III: Vectors and projection
Spaces
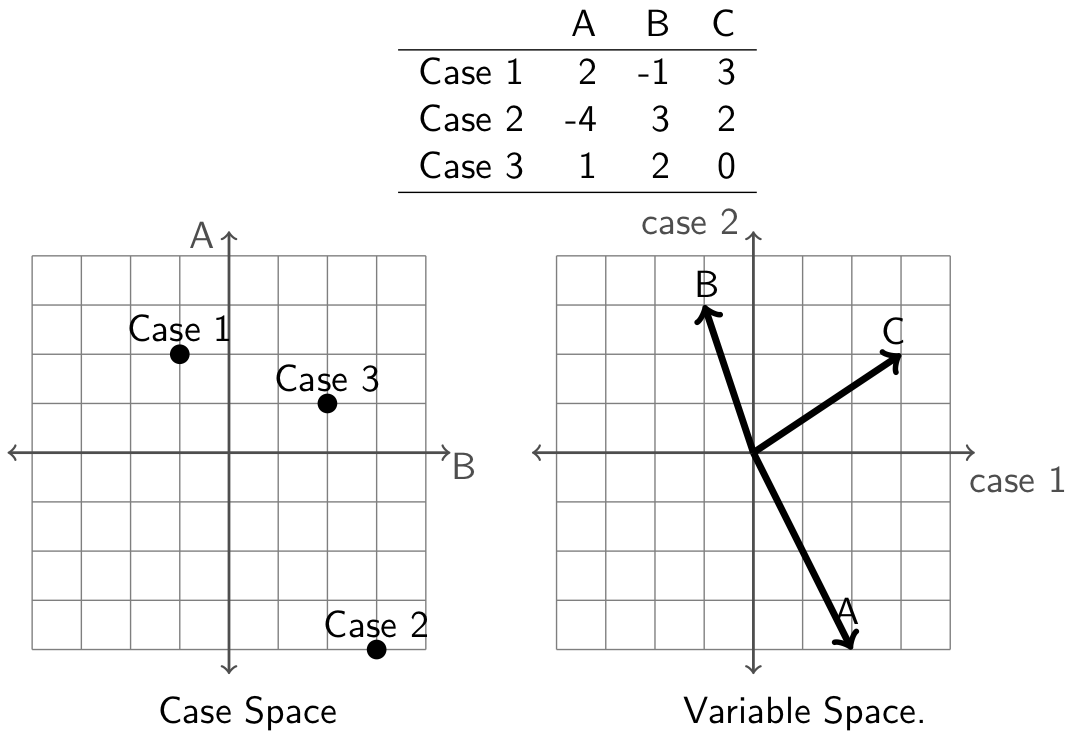
Solving simultaneous equations

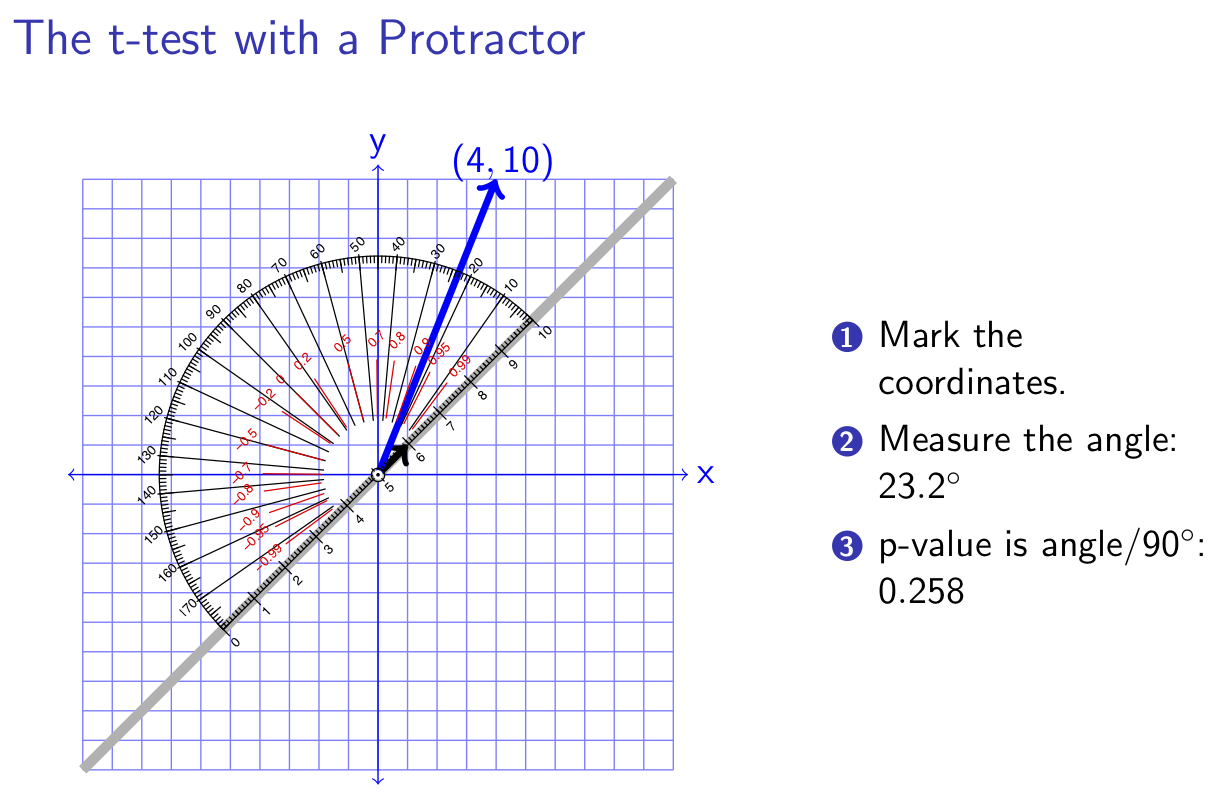
The t-test
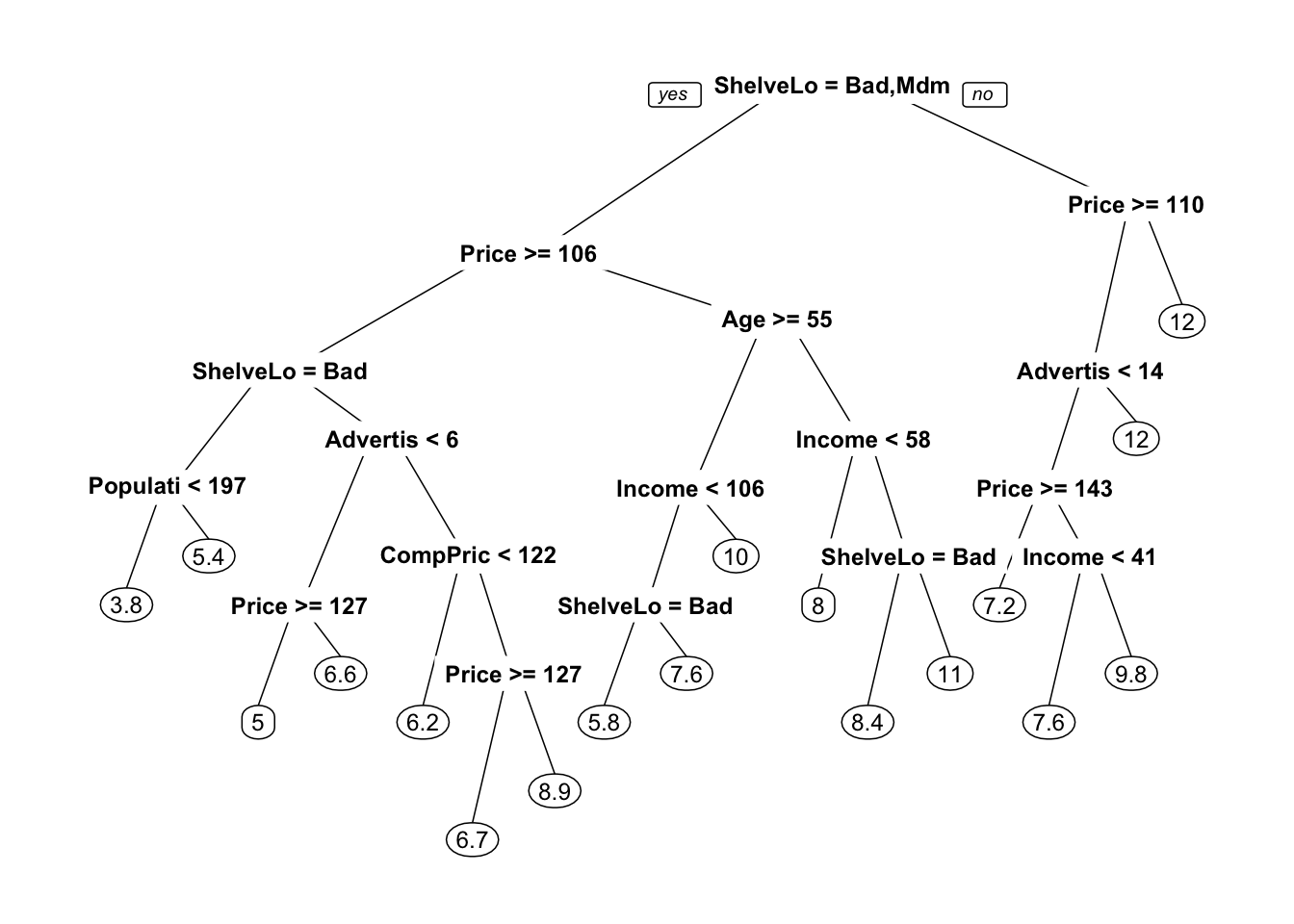
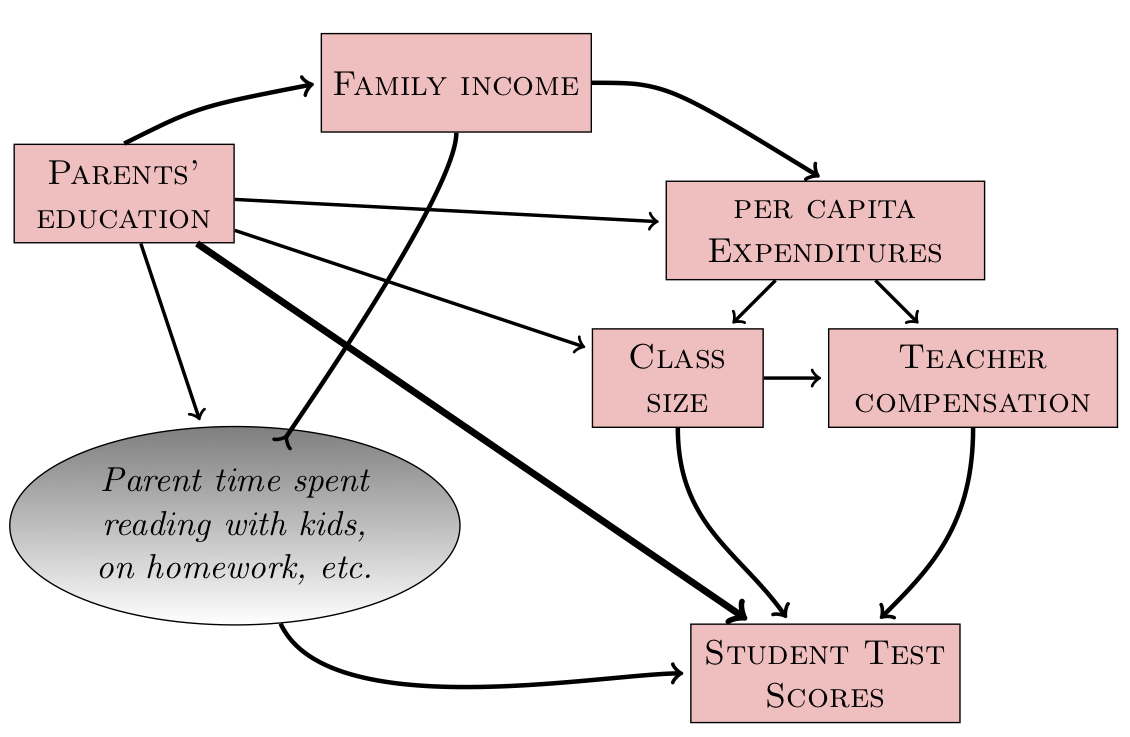
Math Topic IV: Trees and graphs

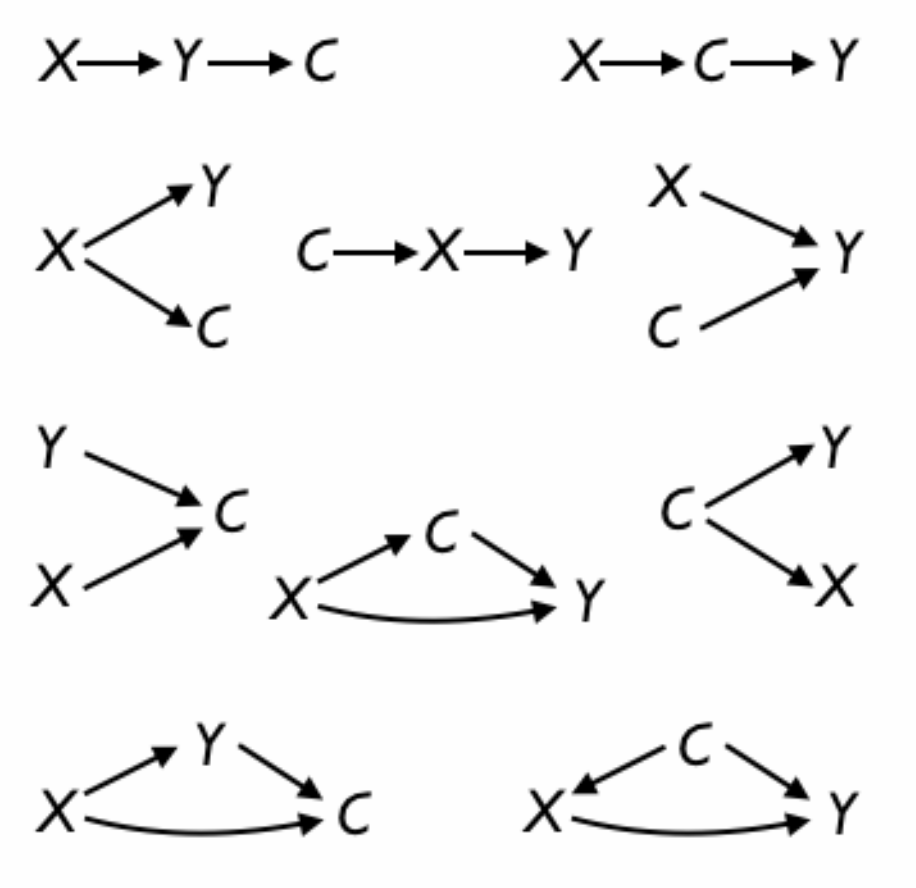

Math Topic V: Operator composition
Modern (since 1970!) data manipulation is done with small set of single-input relational operators:
- select
- project
- filter
- summarize
- group by
- arrange
- pivot wide/narrow
… and one multi-input relational operator:
- join
Database queries consist of composing one operation on top of the previous.
For examples and instruction, see Data Computing
Math Topic VI: Linear combinations of functions
WARNING: You’re going to see some polynomials as examples of linear combinations.
- Do not factor them, find roots, …
- Do not go beyond second order
- and even then, use well behaved basis functions like natural splines
- As a rule use at least two explanatory variables


Math Topic VIII: Computing
Perhaps you don’t think that computing is part of mathematics … but it has notation and abstraction and makes use of many mathematical concepts.
And there are basic computing concepts that are essential to statistics but that are absent from university-level maths: randomization, iteration, accumulation.
- Data, URLs, query strings
- Wrangling: See topic V.
- Graphics: composing multi-layer graphics
Regex: for the puzzle-solving addict
- Functions and operations on functions
- arguments and values
- solve (invert), effect size, optimize, accumulate,
- Randomization
Iteration and accumulation
Summary
- Statistics does not have to be about the canonical tests, and should not be.
- Contemporary uses of data and models are multivariate and involve computing: training models, comparing and interpretting models, graphical presentation.
- The mathematics behind modern uses of data and models involves topics found in the contemporary advanced mathematics curriculum and which, experience demonstrates, are accessible to almost all students without algebra.
There’s low-hanging mathematical fruit for the picking.